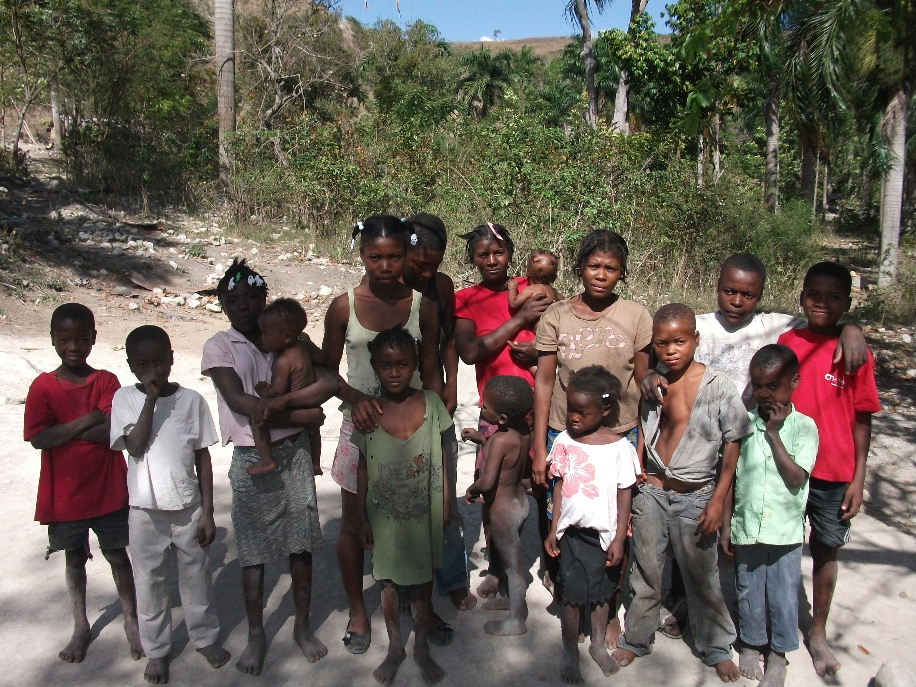
Bwawouj is an oval valley, bordered on the north by a steep ridge that overlooks the major market in Regalis, in Ench. On the south, it is enclosed by another high ridge, this one slicing through Tit Montayn, from east to west. From our base camp in Zaboka, it takes almost two hours to get to the edge of Bwawouj — two difficult hours — and that base camp is already a four-hour hike from Viyèt, the closest our motorcycles can reach.
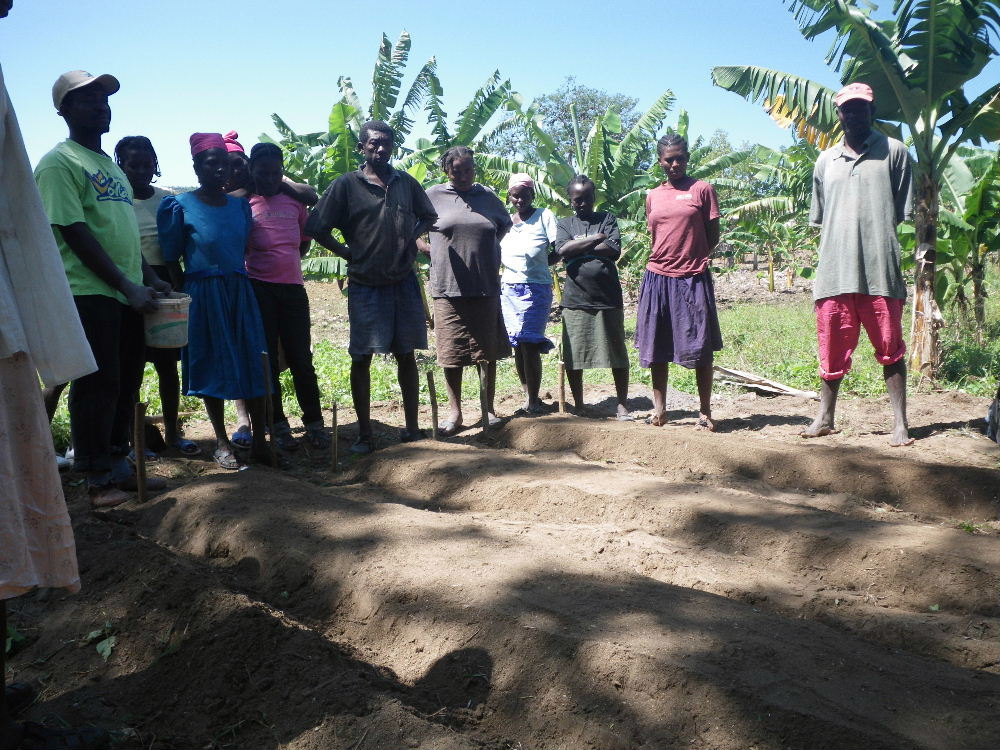
So, Bwawouj is one of the remoter parts of our territory. Orweeth is our case manager there, though he generally goes by a nickname, “Baba.” He’s been spending his Tuesdays in Bwawouj since January 2011. It’s a high-pressure situation because we have very little hope of helping our members there any time between visits. Baba has been struggling together with about a dozen CLM members as they’ve worked to build up their assets — mostly livestock — and learned to live better, healthier lives. Towards the end of June, the members in Bwawouj are scheduled to graduate from our program. They should be able to feed their children well, have asset bases large enough to help them weather a shock, and plans that will enable them to continue improving their lives after CLM leaves.
But the progress that CLM members make is always fragile. Their lives change dramatically during the program’s eighteen months, but the majority remain very poor. And though they can weather much more of a shock than they could have before we met them, they are still very far from anywhere that one would really like them to be. As we help these members move towards graduation, we struggle with them and the difficulties, both large and small, that continue to stand in their way.
Mirlène lives with her husband, Orélès, near the top of the ridge that looks down on Regalis. Their home is about as out-of-the-way as we get. They had two little girls, a five-year-old and a baby, just over one. A couple of weeks ago, the baby got sick. She had a fever and diarrhea, nothing very uncommon for a baby here.
Orélès reacted quickly. He ran to the midwife who had delivered the baby, convinced that his daughter was sick because he hadn’t yet paid the midwife’s bill. What the midwife said to him is worth quoting exactly. “Dlo a gaye, men kanari a la.” That means, “The water’s been spilled, but the pitcher’s still there.” It was a way to say that the baby was going to die, that Orélès should see to the mother instead. The midwife told him that he need not bother to bring the baby to a doctor. “Se pa yon maladi doktè.” That means, “It’s not a medical sickness,” and it is a way to say that the disease is related to some sort of mystical curse.
Orélès rushed back home to find the baby dead and his wife feeling sick. He and Mirlène struggled to plan a decent funeral, borrowing about $20 for a casket and almost twice as much for other funeral expenses.
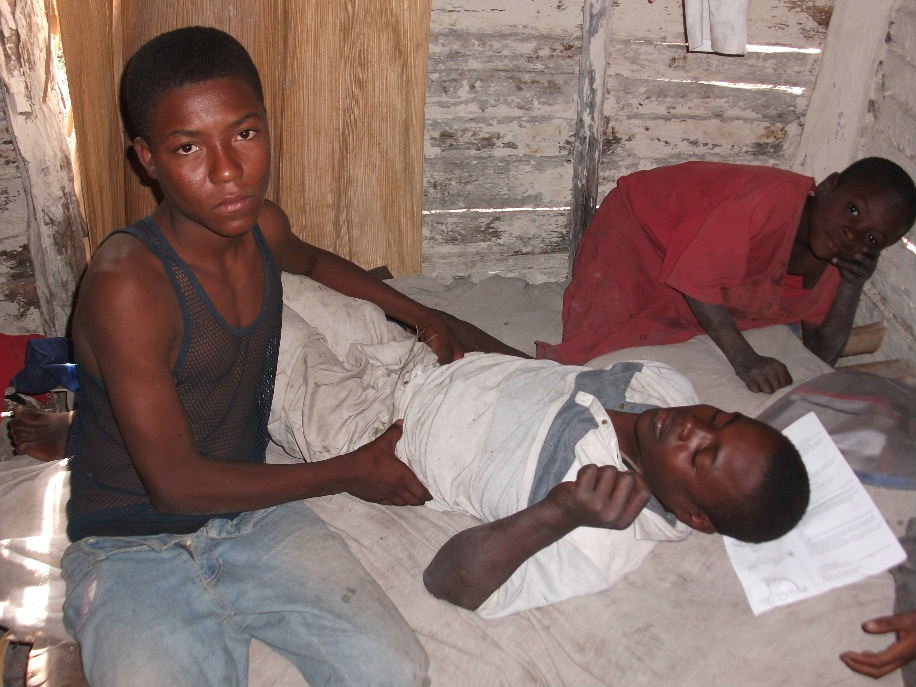
By the time they had buried their daughter, Mirlène was really sick. Orélès ran with her first to a small clinic in Regalis, run by World Vision. It’s almost two hours from his home, but superior and less expensive care at a Partners in Health clinic is at least twice as far.
He bought all the medications the World Vision team prescribed, but then watched as his wife’s state continued to deteriorate. So he spoke to a friend who told him about a very skilled Vodoun practitioner in an area called Nan Chanbo, on the eastern end of Tit Montayn. It would be a long hike, but his friend assured him that the healer would be able to help Mirlène. He thought about the midwife’s claim that the sickness was not medical, and decided to bring his wife to Nan Chanbo. She’s still there, but is apparently recovering well. She should be ready to leave the healer’s home in a few days.
But now they have significant expenses to manage, expenses that could easily derail their progress forward. The $60 for the funeral is only part of the problem. The Vodoun healer assesses two separate fees. Orélès will have to pay about $30 just to take his wife home. After that, he will owe about $190 more as a final bill. That larger sum he will pay in five installments, coming once a year to the healer’s Vodoun festival in December with one-fifth of the fee as a tribute.
So even though they can carry that main fee as a long-term debt, they would need about $90 right away, and the only place they could generally look is towards their livestock. They have a substantial crop of beans that will generate some money if the harvest is good, but it won’t be ready until July. They could sell a couple of goats to get themselves out of the hole they are in, but we don’t want them to do that because their goats are the key to the asset base that we want them to develop.
Fortunately, there is a solution. We budget a small amount of money for emergency expenses. It’s a fund conceived just for cases like this: sudden expenses that risk throwing a member back into the extreme poverty she has struggled to rise out of. We have arranged to meet Orélès in a nearby market tomorrow morning, and will give him the money he needs to eliminate his immediate debts. He’ll still have to finish paying the healer, but he and Mirlène will have five years to take care of that.
In the meantime, they can continue to build up their assets. They are ready to buy a horse, which will enable Mirlène to start up a small commerce in the markets across the mountains as soon as she feels able. We cannot help her or Orélès with the grief that they feel, but we can support them so that they stay on their feet as they move forward on the path out of poverty.
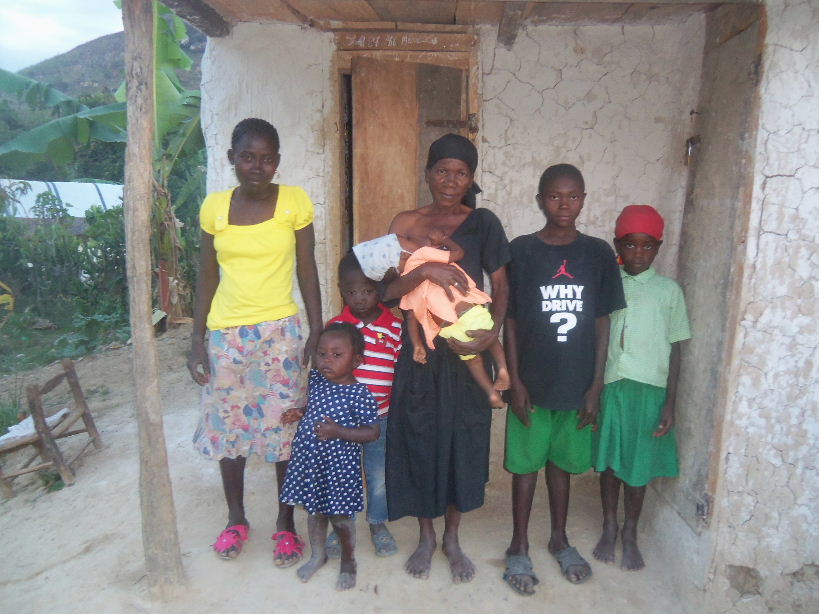
Sephilia’s case is more complicated. She’s an older woman who’s raised eight children, seven of her own and an orphaned niece. All eight are married. Sephilia would not have qualified for CLM, but one of her sons was abandoned by his wife, who left their daughter behind. She became Sephilia’s ninth child.
We don’t know whether it was his wife’s abandonment or something else, but something drove Sephilia’s son crazy. He spends his days yelling and clapping and making other noise, then hiding behind a fence of straw that he’s built up next to her house. He does no work, but lives on what he can get from his mother. She always shares whatever she has with him, but it’s never enough. He is aggressive towards her, even violent. He threatens her with fists and rocks, and if you challenge him about it, he acts as though he doesn’t know what you’re talking about. She struggles to keep any food in the house at all because he will take anything that appeals to him, claiming that CLM has made her rich and that he is hungry, and then leave her and his daughter to fend for themselves.
But there is some method to his madness. He has never threatened or laid a hand on his daughter. His elderly mother has born the whole force of his violence. And he hasn’t touched the assets that his mother has begun to accumulate, though the goats and poultry would seem vulnerable to damage or theft.
Now, Sephilia is, more or less, ready to graduate. She is much less wealthy than some of her fellow members. She’s an older woman, and cannot work very hard. But she has about enough in assets to meet our minimum criterion, has farmland that she can continue to build wealth with, and a plan to grow. But the life-threat that her son represents puts all of that continuously at risk.
She’s spoken to her other children, and there is a son who would especially like her to simply move into his home. But her other children, she says, want her to stay where she is. They like the fact that they can come by anytime and get a cup of coffee or a little something to eat from their mom.
While this might sound like their selfishness, I think the truth is deeper than that. Her life in the yard in which she raised her children, where her husband’s body rests, means a lot to her. She seems to find much of her sense of worth in the little things that, as poor as she is, she can offer her kids. Though she understands that it makes sense for her to leave her home to live in a place where she’d be safe, and though she could easily bring all her livestock with her, that’s not what she wants to do. She says that her children want her to stay where she is, but she talks and acts as though it is what she herself wants. And it’s hard to blame her.
But it’s also hard to figure out how to protect her from her son. The nearest legal authority is almost two hours away on foot. She has another son and a son-in-law who live within fifteen or twenty minutes from her — there are no closer houses — but they are in their own fields all the time. We haven’t been able to get a hold of them yet. She says that her son-in-law in particular has said he’ll protect her, but that’s not working so far.
So we spent a lot of time with the crazy son while we were up there– talking, explaining, and threatening — trying to communicate how important it is for him to let his mother be. She still doesn’t have a door that she can lock on her new home, and Baba has pushed the carpenter who’s responsible for the door to get it done. But we are not sure what else we can do. We won’t be anywhere near her for almost two weeks, and we just have to hope that things will remain stable until then.






















 The clinic is not a regular part of our program, but we try to develop any contacts that come our way to get our members services that we know they need. Marie Gedéon didn’t feel the need to have her eyes checked. Her vision is good. But she knew we needed to speak with her, so she came by.
The clinic is not a regular part of our program, but we try to develop any contacts that come our way to get our members services that we know they need. Marie Gedéon didn’t feel the need to have her eyes checked. Her vision is good. But she knew we needed to speak with her, so she came by.